All About Cockroaches
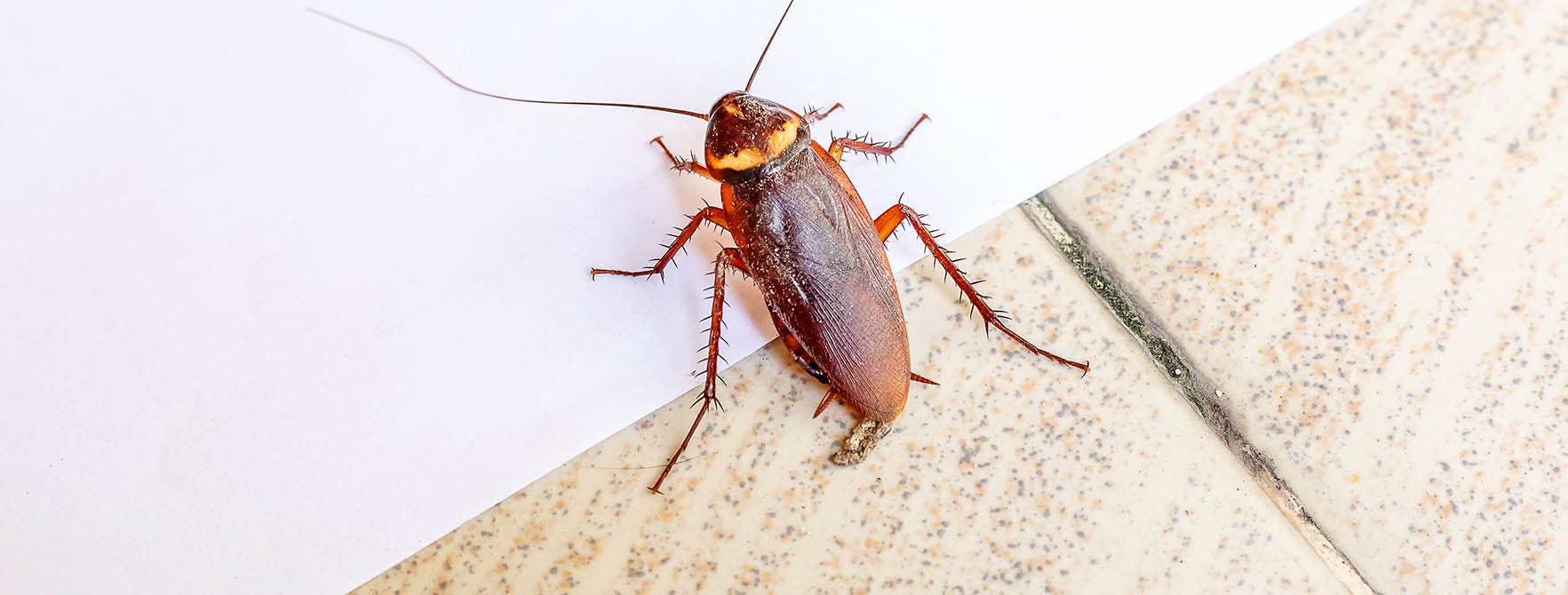

A cockroach infestation brings not only these repulsive insects, but also the threat of E.coli, salmonella, typhoid and a host of other diseases. Learning how to distinguish cockroaches from harmless beetles, as well as the best way to get rid of roaches, is important for anyone battling these bugs.
So... What's a Cockroach?
Cockroaches are oval shaped insects that range from 1/2"-2" in length. Adult cockroaches range in color from tan to reddish brown to black, depending on the species. Nymphs look like smaller versions of adults, and the eggs they emerge from are usually brownish in color and oblong in shape.
Types of Cockroaches

There are three main types we may come across here in the United States - the German Cockroach, the American Cockroach and the Oriental Cockroach.
There are also the Brownbanded Cockroach, Wood Cockroach, and Smokybrown Cockroach, but these are not as common as the other three.
There are 4,000 species of cockroaches worldwide, with 70 identified in the United States. Fortunately, most are quite rare or stay away from human habitation. Three species are most commonly found scuttling about the floors of homes, restaurants and office buildings. Meet your three worst nightmares:
- German Cockroach: German cockroaches are about half an inch long. The body is tan or light brown, typically with two dark brown stripes running in parallel lines down the back. They have long antenna, six legs and an oval shape. German cockroaches prefer temperatures around 70 - 75 degrees, so they just love settling into your home or office. They hunker down into small cracks during the day, usually places where they have a wall on either side such as between the kitchen cabinet and stove, or the cabinets and the refrigerator. At night, they forage for food and water. They feed on tiny scraps of food found on counters, in sinks and on floors.
- Brownbanded Cockroach: The brownbanded cockroach is the second-most common indoor roach. The body is oval-shaped with the same long antenna, but they are a dark brown color with a light tan band around the outside and on the wings. Unlike the German roach, brownbanded roaches like it warm and dry, so you’ll find them near heaters, furnaces, electrical outlets, television sets and radios. They need temperatures around 80 degrees and are also nocturnal insects. They also prefer to rest on high spaces, so they’ll hide on top of cabinets or doorframes during the day.
- American Cockroach: American roaches are about two inches long and a dark, reddish-brown color. They’re oval-shaped with the same telltale long roach antenna. Unlike their cousins the German and brownbanded roach, American roaches prefer living in wet environments, but they will enter homes and other buildings for food. They live in sewers, barns, manure piles and similar places teeming with harmful bacteria, which they can carry onto surfaces that people come into contact with.
These three types of cockroaches are the most common indoor roaches, and the ones most homeowners end up battling when faced with cockroach infestations. It’s important to correctly identify the roach species invading your home. This way you can get rid of roaches targeted to individual species and habitats.
The Cockroach Life Cycle
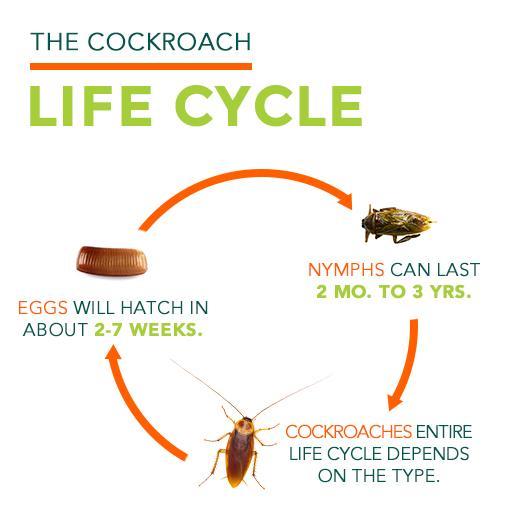
The cockroach, which has existed on this planet much longer than humans, has a basic life cycle involving three stages: egg, nymph and adult. Adult females lay up to 40 eggs at one time, which are encased in an oblong, bean-shaped egg case. The eggs will hatch in about 2-7 weeks, depending on the species of cockroach, and nymphs will emerge.
These nymph undergo a molting process which occurs in stages and can take anywhere from 2 months to 3 years before it becomes a mature adult ready for mating and egg-laying. The length of the entire life cycle depends on the species of the cockroach and the state of its environment.
If you see one roach, chances are good there are thousands living nearby. One female roach can breed just once and stay pregnant for life. You might feel sorry for her, except that the egg sacs she develops on her abdomen each contain 30 new roach nymphs. She’ll deposit these sacs around your home every few weeks. At the end of a year, she can give birth to 30,000 young.
The brownbanded cockroach is also prolific. Females glue egg cases to ceilings, underneath furniture and on carpet; the eggs need a dark place to incubate. Eggs hatch after several weeks. Each female can produce 600 young per year. She’ll never beat the German cockroach’s procreative record, but that’s still one roach too many to have roaming about your home.
American cockroaches produce an egg capsule each week, and they drop it in a warm, moist, dark place near a food source. Each egg capsule contains approximately 14 eggs — she lays 15 to 90 capsules per year. That can quickly add up to 800 or more offspring per year.
Why Cockroaches are Difficult to Kill
Roaches are tough, and difficult to get rid of in your home. Understanding why they’re so tough can help you arm yourself for battle against them.
For example, roaches can live for a month without food and up to two weeks without water. They can also hold their breath for up to 40 minutes, and live for up to a week without their head. Talk about survival skills.
Don’t be disheartened by these facts. Even the most tenacious enemy has a weakness, and with roaches there are several weaknesses that you can exploit in order to kill them. The good news is that natural predators and natural methods of pest control are effective against cockroaches.
Natural Roach Predators

Several natural predators dine on roaches in the wild. Natural predators of cockroaches include:
- Toads
- Frogs
- Geckos
- Iguanas
- Parasitic wasps
Parasitic wasps do not eat the roaches themselves, but lay eggs on the roaches. As the eggs hatch, the wasp nymphs eat the roach. Parasitic wasps also kill tomato hornworms and many other insects this way, keeping in check the population of so-called bad bugs in the home garden.
A naturally occurring fungus called entomopathogenic fungi has also been identified as a way that nature keeps the cockroach population in check. As roaches roam about the woods and fields, spores from the fungus attach to their bodies. The spores kill cockroaches within weeks. Roaches will also transmit spores to one another, passing along the lethal dose to unsuspecting comrades.
Why Roach Infestations are Dangerous
Few will disagree that roaches are repulsive; but are they dangerous? The answer is yes.
Roaches carry 33 types of bacteria and six types of parasites. The spines on their legs add extra surface area, which easily picks up bacteria and parasites from the surfaces they touch. They also eat garbage, sewage and anything else they can find, which passes through their system and into your house when they defecate. If that’s not bad enough, bacteria that can make people sick doesn’t faze the hardy cockroach.
The American cockroach lives in sewer systems, manhole covers and steam tunnels in urban environments, and in animal barns and manure piles in rural ones. Think about what those six legs and myriad leg spines are touching as they run about. These environments are teeming with all types of bacteria, especially E.coli and salmonella. When the American roach picks up this bacteria on its feet, it easily transmits it onto other surfaces including counters, sinks and places where food is prepared. It can also transmit bacteria onto crops such as lettuce, spinach and berries. If these crops aren’t washed adequately, a food poisoning outbreak can occur.
Cockroach feces and skin also contain materials that cause allergies in people, especially in children. Roaches have been linked to increased incidences of asthma, especially among children living in urban environments.
Roaches cause extensive damage to the areas they infest. Several types of roaches enjoy eating glue from envelopes, stamps and book bindings, and can damage paper and leather. Their excrement also leaves a foul odor behind and can damage fabric.
Do Cockroaches Bite?
When cockroach infestations are so severe that they run out of food scraps and sewage to eat, they’ll try to eat meat, including human flesh. They will eat living people as well as dead ones. Roaches will nip at eyelashes, fingertips and fingernails. This has been documented on seagoing vessels; sailors reported that roaches were so numerous, they had to wear gloves to stop them from biting their hands.
More recently, people living in extreme poverty and unsanitary conditions have reported roach bites on their children, who are more vulnerable to bites because they cannot move away fast enough from a roach.
Cockroach bites don’t contain poison, but they can contain bacteria. They can cause swelling, irritation and infections.
Luckily for people, roaches much prefer to dine on food scraps, garbage and sewage to human beings. However, if someone tells you that roaches bite and you’re skeptical, the answer is yes, they can and do bite.
How to Get Rid of Roaches

Now that you’ve identified roaches and understand the danger of an infestation, it’s time to get rid of them. Before reaching for a spray can of pesticides, it’s important to understand two facts:
- Just killing the roaches you can see won’t eliminate the problem
- You’ve got to get rid of their food sources in order to permanently evict them from your home
The roaches that you encounter when you snap on the kitchen light at night are just the tip of the roach-filled iceberg. For every one roach that you see, thousands more are lurking behind the walls, between the counters and everywhere in between.
The best way to get rid of roaches is to take a holistic approach to pest control:
- Eliminate food sources: Roaches live off of scraps and waste. Eliminate every source of possible meals for the roaches. Take out the trash frequently, and wash all cans, bottles and containers before placing them in recycling bins or trash cans. Scrub your kitchen frequently, and clean all surfaces of crumbs and debris daily.
- Eliminate water sources: Roaches also need water, so stop the dripping taps and dry up any moist areas in your home.
- Check your houseplants: Roaches may lurk around houseplants. The water seeping from flowerpots offers an attractive drinking fountain for roaches. You may need to repot your houseplants to remove nymphs and eggs near the plants or soil.
- Stop new roaches from entering: Stop new roaches from entering your home by caulking windows, doors and around incoming pipes such as water, gas and electrical lines. Roaches can enter through tiny holes, so make sure caulking seals the area tightly.
- Use glue traps: One of the most effective ways to monitor and remove roaches naturally is the use of glue traps. Victor® Insect Glue Board packages offer a convenient way to trap roaches without using poisons that can harm children or pets.
- Deep clean: Roaches love bathrooms, kitchens and basements. These rooms provide warm, moist and dark environments as well as plentiful food. Roaches can also deposit egg cases throughout your home. Vacuum all furniture and carpets. Make sure you vacuum under the furniture too, and run the upholstery attachment over sofas and chairs from top to bottom. Take out the cushions and vacuum the interior of upholstered furniture, too. Do this when you notice roaches and after treating your home to sweep up any remaining eggs and nymphs.
- Eliminate clutter: Cluttered environments give roaches places to hide as well as food sources. If you have stacks of old newspapers or magazines, get rid of them. The less clutter in your home, the easier it is to see roaches and other invaders.
All of these methods will help you get rid of cockroaches. You’ll need to use more than one method to truly contain a cockroach infestation. Eliminating their food and water sources, as well as using sprays and traps, should contain or eliminate roaches.
If despite your best efforts you can’t seem to get ahead of the roaches, it may be time to call in a professional pest-control firm. Commercial pest-control products such as boric acid are effective against roaches. Bait traps are also effective. Do not use boric acid powder around children or pets; it’s poisonous.
Do Roaches Offer Any Benefit?
Everything in nature is interconnected, and even scavengers like vultures have their place in the natural order. Roaches do, too. They’re nature’s recyclers, mopping up wastes, eating decaying plants and manure, and generally helping to break down natural elements. Although inside your home they’re more harmful than helpful, they do have their place in the world’s ecosystem alongside other insects that help break down decaying matter into components that nature can use to rebuild.
How to End a Cockroach Infestation
A roach infestation begins when a single female finds a welcoming environment. Roaches can enter your home through tiny cracks in the walls or doors, or even hitching a ride in a grocery store bag. Although figuring out how they got into your home in the first place is important, what’s even more important is taking swift action to end cockroach infestations promptly. With these tips on how to get rid of cockroaches naturally, it’s bye-bye roach and hello peace of mind.
Cockroach Controls
What?
Methods of controlling cockroaches include baits especially those made with boric acid or diatomaceous earth, glue trays, pheromone traps, and sprays containing mint oil, pyrethrin/d-limonene.
How?
Boric Acid is deadly to ants, roaches, and other crawling insects. Some boric acid products contain a food and or pheromone attractant. When using straight boric acid, mix a small amount of boric acid to foods cockroaches will eat. Sweet or greasy foods usually attract them. Cockroaches will take some of the boric acid back to their colony. The colony can be severely damaged or eliminated.
Although boric acid is relatively nontoxic, keep it away from children and pets. It should be enclosed in a bait station or placed in an area inaccessible to children or pets.
Diatomaceous Earth (DE) is a dust-like product that contains the crushed fossilized remains of diatoms. The dust is ingested by the cockroach and affects the cuticle of the cockroach, resulting in its dehydration. The best part about DE is that insects cannot develop a resistance to it since there are no chemicals to which they can develop an immunity. If the area where the DE is applied becomes wet, it will need to be reapplied.
Glue traps have a sticky surface that prevents the cockroaches from escaping once they have ventured onto the trap. These traps are easy to use, since you only need to release the paper that protects the glue surface and place the glue trap along the cockroach trail.
Pheromone traps lure cockroaches as well as other crawling insects, and once inside the trap, the insects cannot escape.
Safer® Brand offers a variety of roach control products to help organically control and eliminate this disease-carrying pest from your home. Products such as Safer® Brand Ant and Crawling Insect Killer Diatomaceous Earth Powder are ideal for cockroach control in your home.
Carefully read and follow all product label instructions completely for safe and effective application.
When?
The bait may take a few days to take effect before results are noticed.
Spray Insect Killing Soap & Pyrethrin as a contact killer. Use in accordance with directions on the product label.
Natural Predators
What?
Cockroaches do have predators, however these predators live outdoors for the most part, and you would not want to let any of them loose in your house to catch the cockroaches. These predators include wasps, centipedes, salamanders, lizards, frogs and toads, bats, birds and some small animals.
How?
In the wild, these predators kill and eat the cockroaches.
When?
The availability of the predators depends on the climate and location of an area. Hibernating animals would not be present in the winter months to prey on cockroaches.

